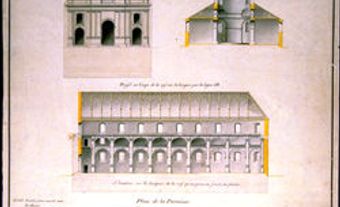
First Religious Buildings on Notre-Dame Street
When Ville-Marie (later to become the city of Montréal) was founded in 1642, a small chapel was built inside the stockade, at la Pointe-à-Callière, and the Jesuits who took charge of it dedicated it to the Virgin Mary (Notre Dame, meaning Our Lady) When a community of Sulpician priests later arrived from France, the need arose to replace the small chapel with a more imposing church. The task of drawing up the architectural plans for the new structure was entrusted to a member of this community, François Dollier de Casson (1636–1701). He designed it in the Baroque style, and it was built on Notre-Dame Street over the period 1672 to 1683.

Construction of the Current Basilica
By 1800, the population of Montréal had grown so much that the existing church on Notre-Dame Street had become too small to meet the parish’s needs. The parish council, with the help of the Saint-Sulpice Seminary, decided to construct a new building and entrusted its design to architect James O’Donnell (1774–1830) of New York City. O’Donnell decided to design the new Notre-Dame Church in the Gothic Revival style then so much in fashion in Europe and the United States.
Construction of the building in this style proceeded despite the vigorous objections of Abbé Jérôme Demers, a Roman Catholic priest and architect from Québec City, whose tastes in architecture were rather traditional. He denounced Gothic Revival for its supposed Protestantism, as well as the rectangular floor plan (with no apse or transepts) that O’Donnell had chosen for the church. But O’Donnell’s design would have a decisive impact on the history of architecture in Canada. For the next 100 years, the Gothic Revival style was closely associated with the religious buildings put up by almost every Christian denomination in the country.
Construction of on the new Notre-Dame Church—the present-day Basilica—began in 1824 and was completed in 1829, and it was consecrated on 15 July 1829. The building can accommodate 8,000 to 10,000 worshippers and remains to this day the largest church in North America. But O’Donnell never lived to see his work completed; he died on 28 January 1830, while its interior was still being decorated. He had converted to Roman Catholicism a few months before his death, and he is buried in the crypt of the church he built.

The two towers that the architect had designed for the front of the church also were not completed until more than 10 years after his death. The western tower, nicknamed Perseverance, was completed in 1841, under the direction of John Ostell (1813–1892). It still houses a great bell whose weight is estimated at 11,000 kg. In 1843, the eastern tower, nicknamed Temperance, was completed; it houses a 10-bell carillon.
Interior Renovations and Redecoration in the 20th Century
Starting in 1872, the interior of the church was redecorated under the direction of Montréal architect Victor Bourgeau (1809–1888), who chose colours and motifs reminiscent of the interior of Sainte-Chapelle in Paris. The process of transforming the sanctuary and the confessionals, installing new mouldings and painting them took nearly 10 years. The 1880s saw further changes, notably the construction of a pulpit 14 metres high, sculpted by artist Louis-Philippe Hébert (1850–1917), as well as the installation of icons and sculptures and the replacement of all the pews.
In 1889, a new chapel, Notre-Dame du Sacré-Cœur, was added to the church, for ceremonies with smaller numbers of congregants. It was consecrated on 8 December 1891, and the great organ commissioned from Casavant Frères was also consecrated that same year. The chapel was damaged in a fire in 1978 and rebuilt in 1980. It now houses a bronze altarpiece that is the work of Québec artist Charles Daudelin, along with a barrel organ from Guilbault-Thérien Inc.

Notre-Dame Church has seen thousands of religious ceremonies and events over the years, including the funeral of Sir George-Étienne Cartier in 1873 and the Eucharistic Congress of 1910. To mark the church’s centenary in 1929, large decorative street lamps were installed in its forecourt, and in 1930-31, a series of commemorative stained-glass windows were put in place. The baptismal fonts were finely decorated by the painter Ozias Leduc (1864–1955).
Throughout the 20th century, various alterations changed the appearance of the church. The most important of these was probably the installation of the altar at the centre of the sanctuary, a change brought about by the Second Vatican Council.
Heritage Recognition
On 21 April 1982, Notre-Dame Church was declared a minor basilica by apostolic brief. Its historical, architectural and artistic value, as well as its religious importance, were thus recognized. In 1984, Pope John Paul II visited the Basilica, and in 2000, the funeral of former prime minister Pierre Elliott Trudeau was held there. In 1989, the Basilica was designated a national historic site of Canada. It is also included in the Site patrimonial de Montréal, the provincially-designated heritage site in Old Montréal, comprising the former walled city, plots of land in the former outlying districts, the Pointe-à-Callière district, and the Old Port. The area around the Basilica and beneath its forecourt also contains archaeological treasures of great ethnological value (see Pointe-à-Callière, the Montréal Museum of Archaeology and History).
Despite its importance for tourism (it receives some 2,500 visitors per day in peak season), the Basilica continues to fulfil its religious mission. It is a place of worship where over 120 baptisms and over 120 marriages are celebrated every year.
Because of the Basilica’s remarkable acoustics and its great organ, numerous concerts are presented there by renowned orchestras, including the Montreal Symphony Orchestra. Every summer since 2004, the Basilica has hosted the International Organ Festival at Notre-Dame of Montreal. Since 2008, it has also hosted various activities as part of the Canadian International Organ Competition, one of whose objectives is to increase public awareness of the great organ and the heritage building that houses this exceptional instrument.
See also Architectural History: 1759-1867; Collegiate Gothic and Other Revival Styles in 20th-Century Canadian Architecture

 Share on Facebook
Share on Facebook Share on X
Share on X Share by Email
Share by Email Share on Google Classroom
Share on Google Classroom