Article
Aberdeen Lake
Aberdeen Lake, 1100 km2, elev 80 m, maximum length 91 km, is located in Nunavut, 213 km south of the Arctic Circle.

Enter your search term
Signing up enhances your TCE experience with the ability to save items to your personal reading list, and access the interactive map.
Create AccountArticle
Aberdeen Lake, 1100 km2, elev 80 m, maximum length 91 km, is located in Nunavut, 213 km south of the Arctic Circle.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
Allison Pass, elevation 1,352 metres, is located at kilometre 60, the highest point on the Hope-Princeton Highway (opened 1949) through the Cascade Mountains of southern British Columbia.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
The Alsek River originates in the highest mountains in Canada, the St Elias Range.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
Amadjuak Lake, 3115 km2, elevation 113 m, is one of 2 lakes situated in the Great Plain of the Koukdjuak in south-central Baffin Island. This lower-lying area only emerged recently (in geological terms) from beneath the waters of Foxe Basin. Amadjuak Lake is the third-largest in Nunavut.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
Amund Ringnes Island, 5255 km2, located between Ellef Ringnes and Axel Heiberg islands in the Arctic Archipelago. It is flat (highest point about 610 m) and windswept; in winter its coasts are virtually indistinguishable from the surrounding ice.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
Anderson River, 692 km long, originates in a group of lakes north of Great Bear Lake in the Northwest Territories and meanders north and west to empty into Liverpool Bay, an arm of the Beaufort Sea, just east of the Mackenzie Delta.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
Following the retreat of glacial ice, about 13 000 years ago, the lowlands were nearly completely flooded by the sea to a height of 30 m.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
Anse du Cap des Rosiers [Fr, "cove of the cape of rosebushes"] was named for the many wild rosebushes found there. The cape that forms the bay is a steep and shrub-covered promontory.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
The overgrowth of lush vegetation has been cleared away from the remains of Ninstints's longhouses and totem poles, which pay silent homage to their creators.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/1c61ad08-f404-4f01-83ee-d9b43e4b833b.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/1c61ad08-f404-4f01-83ee-d9b43e4b833b.jpg

Article
Lying north of mainland Canada, the Arctic Archipelago consists of 94 major islands (greater than 130 km2) and 36,469 minor islands covering a total of 1.4 million km2. Apart from Greenland, which is almost entirely ice covered, the Canadian Arctic Archipelago forms the world's largest High Arctic land area.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/1a2d0ea5-eb83-4b6c-98cc-246ef0adac17.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/1a2d0ea5-eb83-4b6c-98cc-246ef0adac17.jpg

Article
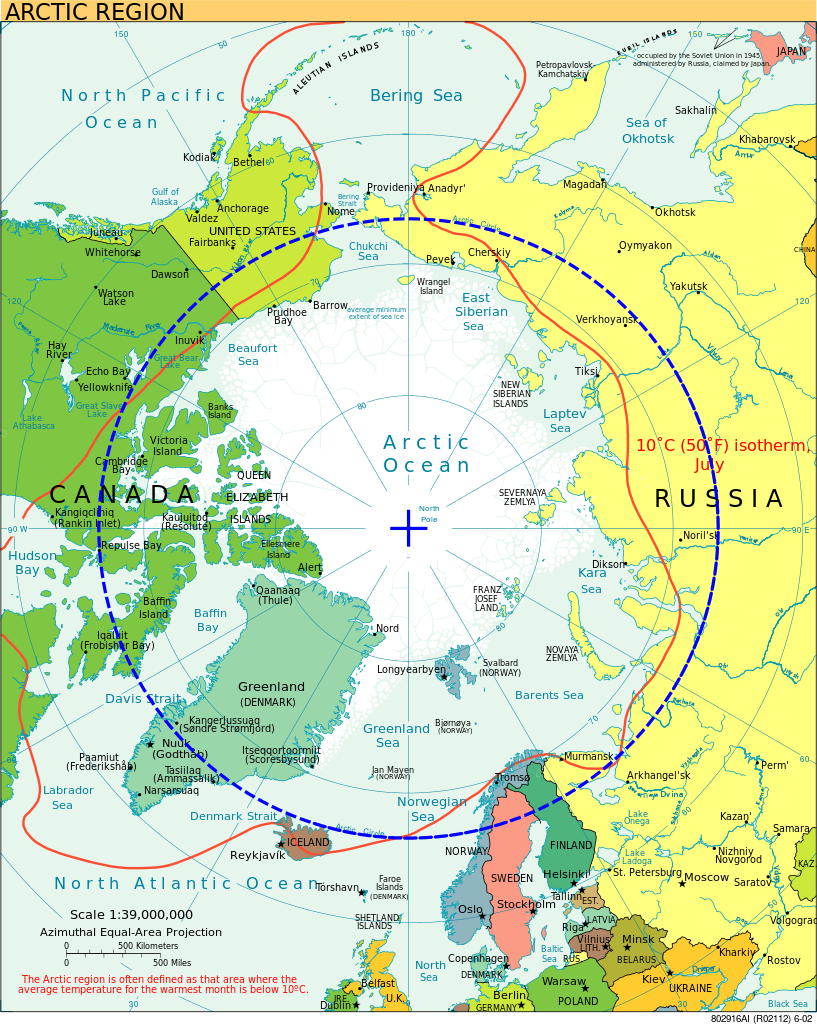
The Arctic Circle is a parallel or line of latitude at approximately 66°33’ N that marks the border of the Arctic, the northernmost region of Earth. The geographic point at the centre of Arctic Circle is the North Pole. In Canada, communities located close to this cartographic boundary include Old Crow in the Yukon, Fort McPherson in the Northwest Territories, and Repulse Bay and Qikiqtarjuaq in Nunavut. The latitude of the Arctic Circle shifts slightly depending on the tilt of the Earth’s rotational axis.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/98ad523f-8b74-429e-864d-27b1e0f18ac9.png" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/98ad523f-8b74-429e-864d-27b1e0f18ac9.png
Article
The Arctic Red River flows 499 km north-northwest from glaciers in the North Mackenzie Mountains, crossing 4 mountain ranges before it winds its way through the Mackenzie Lowlands, crossing the Arctic Circle and joining the MACKENZIE RIVER just south of the Mackenzie River Delta.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
The Assiniboine River, 1070 km long and with a mean discharge of 45 m3/s, rises in southeastern Saskatchewan.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/aab596e1-824f-41f8-aaa0-003d7d08449f.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/aab596e1-824f-41f8-aaa0-003d7d08449f.jpg

Article
Athabasca Landing Trail was established 1875 by Hudson's Bay Company between Edmonton and Athabasca Landing to improve and expand northern transportation.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/86a45811-ca7b-4681-85e6-0f4769979844.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/86a45811-ca7b-4681-85e6-0f4769979844.jpg
