Timelines
Acadians
This timeline highlights events and people related to Acadian History.

Enter your search term
Signing up enhances your TCE experience with the ability to save items to your personal reading list, and access the interactive map.
Create Account"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/Acadians-6.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/Acadians-6.jpg

Article
Alberta, the westernmost of Canada's three Prairie provinces, shares many physical features with its neighbours to the east, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. The Rocky Mountains form the southern portion of Alberta's western boundary with British Columbia. Alberta was named after Princess Louise Caroline Alberta, fourth daughter of Queen Victoria. The province is home to the country’s largest deposits of oil and natural gas.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/251b5d36-82cc-4ec1-80e8-471cfd59098a.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/251b5d36-82cc-4ec1-80e8-471cfd59098a.jpg

Timelines
Alberta, the westernmost of Canada's three Prairie provinces, shares many physical features with its neighbours to the east, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. The Rocky Mountains form the southern portion of Alberta's western boundary with British Columbia.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/412a21a2-aed2-4825-9e29-83935aa5961e.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/412a21a2-aed2-4825-9e29-83935aa5961e.jpg

Article
Lucy Maud Montgomery’s first novel, Anne of Green Gables (1908), became an instant bestseller and has remained in print for more than a century, making the character of Anne Shirley a mythic icon of Canadian culture. The book has sold an estimated 50 million copies worldwide, been translated into at least 36 languages, as well as braille, and been adapted more than two dozen times in various mediums. A musical version first produced by the Charlottetown Festival in 1965 is the longest running annual musical theatre production in the world, while the award-winning 1985 CBC miniseries starring Megan Follows is the most-watched television program in Canadian history. Thousands of tourists visit Prince Edward Island each year to see the “sacred sites” related to the book, and the sale of Anne-related commodities such as souvenirs and dolls has come to constitute a cottage industry.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/3a0688c7-9c5d-46e9-97ac-c132fabdf134.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/3a0688c7-9c5d-46e9-97ac-c132fabdf134.jpg

Article
Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, New Brunswick and Newfoundland constitute the Atlantic provinces.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
R v. Bedard (1971) challenged section 12(1)(b) of the Indian Act, which concerns the rights of Status Indian women in Canada. The appellant in the case, Yvonne Bedard, took the federal government to court after losing her rights as a Status Indian because of her marriage to a Non-Status man. In 1973, before the Supreme Court of Canada, the Bedard case merged with AG v. Lavell, another case concerning gender discrimination (see Status of Women) in the Indian Act. Although Bedard ultimately lost her reinstatement claims, her case inspired future legal battles regarding women’s rights and the Indian Act, including Lovelace v. Canada (1981) (see Sandra Lovelace Nicholas) and the Descheneaux case (2015).
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Editorial
The following article is an editorial written by The Canadian Encyclopedia staff. Editorials are not usually updated. “Freedom and a Farm.” The promise was exciting to the thousands of African Americans, most seeking to escape enslavement, who fought in British regiments during the American Revolutionary War (1775–83). Following the war, they joined tens of thousands of Loyalists — American refugees who had sided with the British. Between 80,000 and 100,000 Loyalists eventually fled the United States. About half came to British North America. The main waves arrived in 1783 and 1784. The territory that now includes the Maritime provinces became home to more than 30,000 Loyalists. Most of coastal Nova Scotia received Loyalist settlers, as did Cape Breton and Prince Edward Island (then called St. John’s Island).
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/be13527b-b76d-408a-afca-30acbd4f7bfc.png" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/be13527b-b76d-408a-afca-30acbd4f7bfc.png

Article
British Columbia is Canada's most westerly province, and is a mountainous area whose population is mainly clustered in its southwestern corner. BC is Canada’s third-largest province after Québec and Ontario, making up 10 per cent of Canada’s land surface. British Columbia is a land of diversity and contrast within small areas. Coastal landscapes, characterized by high, snow-covered mountains rising above narrow fjords and inlets, contrast with the broad forested upland of the central interior and the plains of the northeast. The intense "Britishness" of earlier times is referred to in the province's name, which originated with Queen Victoria and was officially proclaimed in 1858.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/449cfbc9-a5ff-4a70-b1e2-58f5ab29ffa5.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/449cfbc9-a5ff-4a70-b1e2-58f5ab29ffa5.jpg

Timelines
British Columbia is Canada's most westerly province, and is a mountainous area whose population is mainly clustered in its southwestern corner. BC is Canada’s third-largest province after Québec and Ontario, making up 10 per cent of Canada’s land surface.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/08691466-f851-405a-aed3-4dae6f6e6024.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/08691466-f851-405a-aed3-4dae6f6e6024.jpg

Article
The colony of British Columbia was founded in 1858 in response to the Fraser River Gold Rush. (See also The Fraser River Gold Rush and the Founding of British Columbia.) The colony established representative government in 1864 and merged with the colony of Vancouver Island in 1866. In May 1868, Amor De Cosmos formed the Confederation League to bring responsible government to BC and to join Confederation. In September 1868, the Confederation League passed 37 resolutions outlining the terms for a union with the Dominion of Canada. The terms were passed by both the BC assembly and the federal Parliament in 1871. The colony joined Canada as the country’s sixth province on 20 July 1871. The threat of American annexation, embodied by the Alaska purchase of 1867, and the promise of a railway linking BC to the rest of Canada, were decisive factors.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/1f3712f0-f1ac-4fba-a093-ff4c7cfec856.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/1f3712f0-f1ac-4fba-a093-ff4c7cfec856.jpg

Article
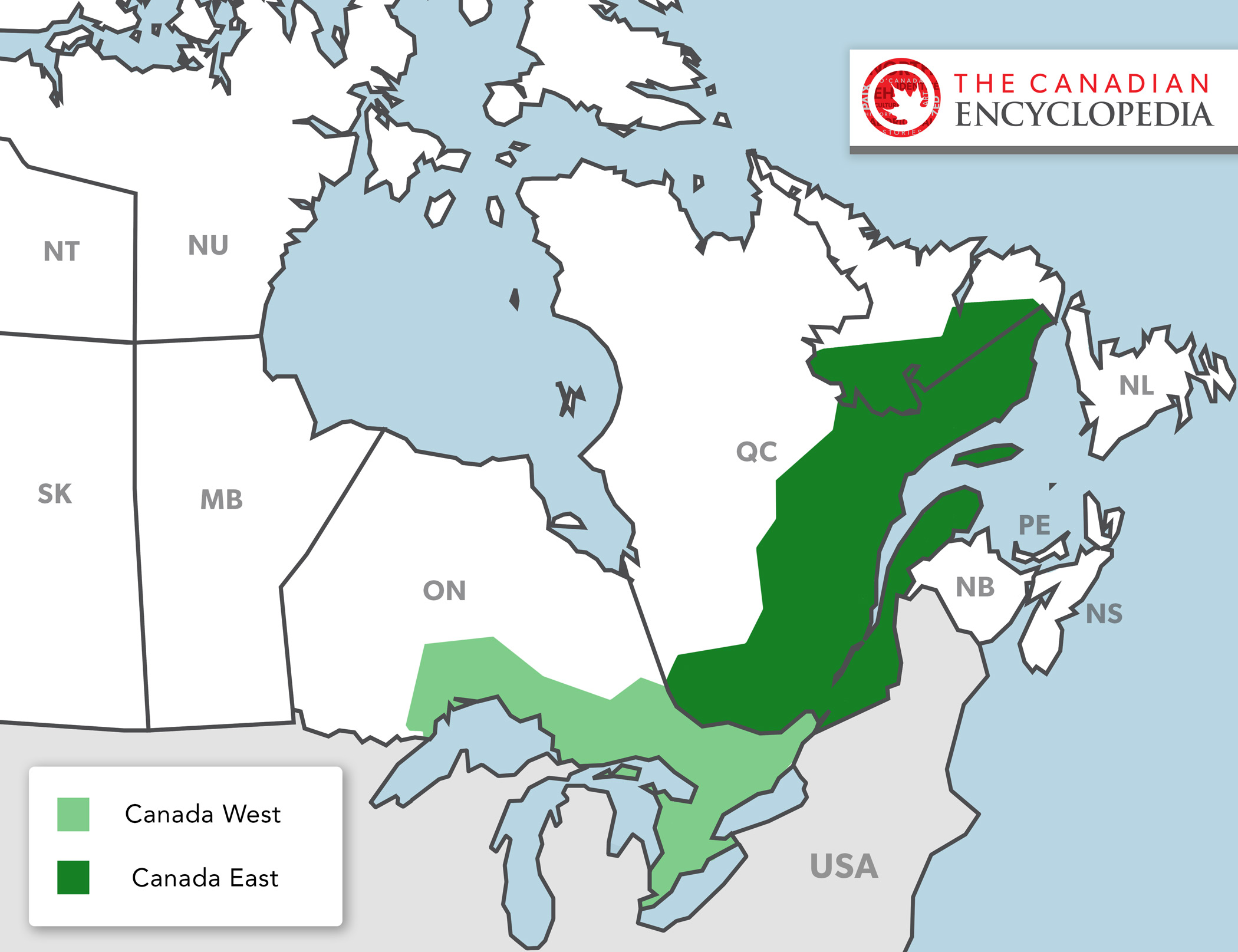
In 1841, Britain united the colonies of Upper and Lower Canada into the Province of Canada. This was in response to the violent rebellions of 1837–38. The Durham Report (1839) laid out the guidelines to create the new colony with the Act of Union in 1840. The Province of Canada was made up of Canada West (formerly Upper Canada) and Canada East (formerly Lower Canada). The two regions were governed jointly until Confederation in 1867. Canada West then became Ontario and Canada East became Quebec.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/new_article_images/PoliticsInOntario/Map_Canada_West_East.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/new_article_images/PoliticsInOntario/Map_Canada_West_East.jpg
Article
In 1841, Britain united the colonies of Upper and Lower Canada into the Province of Canada. This was in response to the violent rebellions of 1837–38. The Durham Report (1839) laid out the guidelines to create the new colony with the Act of Union in 1840. The Province of Canada was made up of Canada West (formerly Upper Canada) and Canada East (formerly Lower Canada). The two regions were governed jointly until Confederation in 1867. Canada West then became Ontario and Canada East became Quebec.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Collection
This collection explores the rich heritage of the Acadians through articles and exhibits, as well as quizzes on arts and culture, history and politics, historical figures, and places associated with the Acadian people.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/0988fc77-c4b5-410f-8147-ffcf8bb53fa6.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/0988fc77-c4b5-410f-8147-ffcf8bb53fa6.jpg

Article
Dominion of Canada is the country’s formal title, though it is rarely used. It was first applied to Canada at Confederation in 1867. It was also used in the formal titles of other countries in the British Commonwealth. Government institutions in Canada effectively stopped using the word Dominion by the early 1960s. The last hold-over was the term Dominion Day, which was officially changed to Canada Day in 1982. Today, the word Dominion is seldom used in either private or government circles.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/143f8587-f938-4cf1-bdc2-c441d02dc962.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/143f8587-f938-4cf1-bdc2-c441d02dc962.jpg

Article
The Fransaskois are francophones living in Saskatchewan. According to recent Canadian statistics, 1.5 per cent of the population (16,373 inhabitants) have French as their mother tongue and 1.3 per cent of the population (14,440 inhabitants) have French as their first official language (see French language in Canada).
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/new_article_images/Fransaskois/Flag_Francophones_Saskatchewan_Fransaskois.png" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/new_article_images/Fransaskois/Flag_Francophones_Saskatchewan_Fransaskois.png
