Acts and Treaties
Acts and Treaties through Canadian history
-
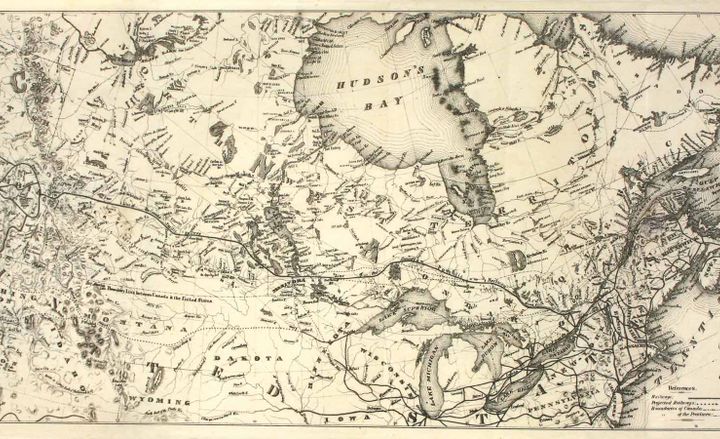
March 29, 1632

Acts and Treaties
Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye
France recovered Québec from England in the Treaty of Saint-Germain, along with compensation for goods siezed when Champlain surrendered Québec.
-
July 21, 1667

Acts and Treaties
Treaty of Breda
The Treaty of Breda provided for French restoration of the English part of the island of St Christopher's, West Indies, in exchange for Acadia, captured from the French in 1654.
-
January 22, 1690

Acts and Treaties
Haudenosaunee (Iroquois) Peace Treaty
The Haudenosaunee concluded a peace treaty with the English and the tribes of the Great Lakes.
-
September 30, 1697

Acts and Treaties
Treaty of Ryswick
The Treaty of Ryswick between England and France provided for the restoration of all Hudson's Bay Co posts seized by Pierre le Moyne d'Iberville.
-
April 11, 1713
Acts and Treaties
Treaty of Utrecht Signed
The Treaty of Utrecht was signed, ending the War of the Spanish Succession. It recognized the claim of the Hudson's Bay Co to Rupert's Land, and Acadia became a permanent English possession.
-
October 18, 1748
Acts and Treaties
Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle
The Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle ended the War of the Austrian Succession. PEI, Cape Breton Island and Louisbourg were returned to France.
-
February 10, 1763

Acts and Treaties
Treaty of Paris 1763
The Treaty of Paris was signed, ending the Seven Years' War. France ceded to Britain all North American possessions except Saint-Pierre and Miquelon off Nfld, and Louisiana (sold in 1803). The treaty authorized freedom of religion in the colony.
-
October 07, 1763
Acts and Treaties
Royal Proclamation
The Royal Proclamation was issued by King George III, setting the western boundary of British settlement following the Seven Years War. Historic, foundational, flawed, the Proclamation stated that Aboriginal title had existed and continued to exist. All land was considered Aboriginal land until ceded by treaty, which could only be annexed by the Crown.
-
May 09, 1781

Acts and Treaties
Niagara Purchase of 1781
The Niagara Purchase of 1781, also known as Treaty 381, was one of the first land agreements between Indigenous peoples and British authorities in Upper Canada (now Ontario). As a result, a 6.5-km-wide strip along the west bank of the Niagara River connecting Lake Erie and Lake Ontario was made available for settlement by Loyalists, who had been displaced by the American Revolution. The Niagara Purchase was one of many agreements made in the 1700s and 1800s that are collectively known as the Upper Canada Land Surrenders.
-
September 03, 1783
Acts and Treaties
Treaty of Paris 1783
This treaty ended the American Revolution, recognizing the independence of the American colonies. The boundary between British and American territories was set along the St. Lawrence River and through the Great Lakes. Post-war life in the United States was very difficult for British Loyalists, who endured property loss and discrimination. Many left and began to arrive in Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Québec and Ontario. Famous migrant Loyalists include Lieutenant James Moody, Laura Secord and Richard Pierpoint.
-
May 22, 1784

Acts and Treaties
Mohawk Families Arrive at Bay of Quinte
During the American Revolution (1775–83), the British promised their allies, the Mohawks, that their homeland would be returned to them after the war. But when the revolution ended, the Treaty of Paris gave traditional Mohawk territory to the United States. The British instead offered the Mohawks their choice of any unsettled land in Upper Canada (now Ontario). They chose land along the north shore of Lake Ontario on the Bay of Quinte. About 20 Mohawk families (100–125 people) travelled by canoe from Lachine and arrived at the Bay of Quinte on 22 May 1784. (See also Crown Grant to the Mohawks of the Bay of Quinte.)
-
August 01, 1785

Acts and Treaties
John Collins’s Purchase of 1785
John Collins’ Purchase of 1785 is one of the oldest land agreements between Indigenous peoples and British authorities in Upper Canada (now Ontario). It concerned the use of lands extending from the northwestern end of Lake Simcoe to Matchedash Bay, an inlet off Georgian Bay in Lake Huron. The purpose was to provide the British with a protected inland water route between Lake Ontario and Lake Huron, away from potential American interference. John Collins’s Purchase is one of many agreements made in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, known as the Upper Canada Land Surrenders.
-
May 20, 1790

Acts and Treaties
McKee’s Purchase of 1790
McKee’s Purchase of 1790 (also known as the McKee Treaty or Treaty 2) was an early land agreement between Indigenous peoples and British authorities in Upper Canada (now Ontario). The southernmost Upper Canada treaty, it consisted of a large strip of territory from the southwestern shore of Lake Erie north to the Thames River and east to a point southwest of modern-day London, Ontario. This land was made available for settlement by Loyalists who were displaced by the American Revolution. McKee’s Purchase legitimized the land transfers of 1784 and 1786 as well as many other private illegal sales of Indigenous land to settlers.
-
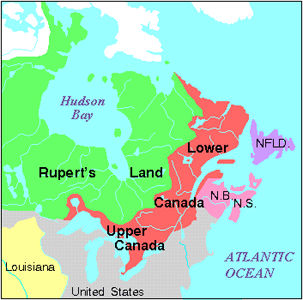
December 26, 1791
Acts and Treaties
Constitutional Act
The Constitutional Act, which created the colonies of Upper and Lower Canada, came into effect. It had been passed 10 June and had received royal assent 19 June. The formal division of the Province of Québec had taken place 21 August.
-
April 01, 1793

Acts and Treaties
Crown Grant to the Mohawks of the Bay of Quinte
Upper Canada Lieutenant-Governor John Graves Simcoe executed Treaty 3½ or the Simcoe Deed to recognize the Mohawks’ contributions to the British during the American Revolution. The treaty granted the Mohawks some 92,700 acres (375 km2) on the Bay of Quinte, an area about the size of a township. However, the government gave Mohawk land to Loyalists, who continued to arrive between 1820 and 1843. As a result, the Mohawk tract was reduced ultimately to 18,000 acres (73 km2).
-
January 11, 1794

Acts and Treaties
Third Nootka Convention
The tug of war between Spain and Britain for control of trade and navigation along the Northwest Coast and in the Pacific Ocean ended with the signing of the third Nootka Convention. Over the course of the three conventions, both nations acknowledged their respective rights to trade at Nootka Sound, with neither permitted to claim total sovereignty or construct permanent garrisons and factories.
-
November 19, 1794
Acts and Treaties
Jay's Treaty Passed
By Jay's Treaty, the British agreed to evacuate frontier posts by 1796. US shipping would have access to British possessions.
-
March 30, 1809

Acts and Treaties
Labrador Act
The Labrador Act gave Labrador to Newfoundland.
-
December 24, 1814
Acts and Treaties
Treaty of Ghent
Peace talks between Great Britain and the United States took place in Belgium in August and ended with the signing of the Treaty of Ghent on Christmas Eve. The British insisted the treaty be ratified by both governments before it took effect because the Americans refused to ratify three previous treaties.
-
April 28, 1817
Acts and Treaties
Rush-Bagot Agreement
This agreement demilitarized the Great Lakes and, along with the Convention of 1818, solidified the border between the United States and British North America.
-
October 20, 1818

Acts and Treaties
Boundary Set at 49th Parallel
The Convention of 1818 described the boundary between British North America and the US as a line from the farthest northwestern point of Lake of the Woods to the 49th parallel and thence west to the Rocky Mountains.
-
August 01, 1834

Acts and Treaties
Abolition of Slavery Act
Black people are now considered British subjects, paving the way for property-owning Black men to vote. But racism and discrimination at polling stations mean many do not cast their ballots. (See Slavery Abolition Act, 1833.)
-
August 01, 1834
Acts and Treaties
Emancipation Day
The Abolition of Slavery Act, passed by the British Parliament in 1833, came into force.
-
July 23, 1840

Acts and Treaties
Act of Union Assent
The Act of Union joining Upper and Lower Canada received royal assent in England. It came into effect on 10 February 1841.
-
February 10, 1841

Acts and Treaties
Act of Union in Effect
The Act of Union came into effect, uniting Upper and Lower Canada into the Province of Canada, a legislative union with 84 members divided equally between Canada East and Canada West.
-
August 09, 1842
Acts and Treaties
Webster-Ashburton Treaty
The frontier between Canada and the US was defined by the Webster-Ashburton Treaty, which was signed by the US and Britain. The treaty also provided for the surveying, mapping and marking of the agreed NB-Maine boundary, and was completed in June 1847.
-
June 26, 1846
Acts and Treaties
Repeal of Corn Laws
Royal assent was given to Robert Peel's Act repealing the Corn Laws, terminating the preferential treatment of Canadian grain in Britain.
-
January 01, 1857
Acts and Treaties
Gradual Civilization Act Passed in the Province of Canada
The government attempts to assimilate First Nations men by offering them the right to vote if they voluntarily enfranchise. This means giving up rights, including treaty rights. Only one person elects to do so under this Act. (See also Indigenous Peoples in Canadian Law.)
-
August 02, 1858
Acts and Treaties
BC a Crown Colony
An imperial Act provided for the government of British Columbia as a Crown colony, to include the Queen Charlotte Islands but excluding Vancouver Island; Victoria was the new capital.
-
August 06, 1866
Acts and Treaties
British Columbia Unites
An imperial statute established the political union of Vancouver Island and the mainland of BC as the colony of British Columbia.
-
May 22, 1867
Acts and Treaties
Proclamation of Confederation
A royal proclamation declared that the Dominion of Canada would come into existence on July 1.
-
July 31, 1868

Acts and Treaties
Rupert's Land Act
The Rupert's Land Act was passed, allowing the Crown to declare Rupert's Land part of the Dominion of Canada.
-
May 12, 1870
Acts and Treaties
Manitoba Act
The Manitoba Act received royal assent. It created the province of Manitoba, Canada's fifth, and went into effect on 15 July.
-
August 03, 1871

Acts and Treaties
Treaty 1
The first post-Confederation treaty was signed at Lower Fort Garry, Man. The first of many “Numbered Treaties,” Treaty 1 was signed between the Crown and the Ojibwe and Swampy Cree Nations. The treaty included the provision of livestock, agricultural equipment and the establishment of schools in exchange for ceding large tracts of Indigenous hunting grounds.
-
August 21, 1871
Acts and Treaties
Treaty 2
Treaty 2 was concluded with Chippewa of Manitoba, who ceded land from the mouth of Winnipeg River to the northern shores of Lake Manitoba across the Assiniboine River to the United States frontier.
-
October 03, 1873
Acts and Treaties
Treaty 3
Treaty 3 was signed by the Saulteaux (Chippewa) of northwestern Ontario and of Manitoba. For the surrender of a tract comprising about 55,000 sq. miles, the Dominion Government reserved not more than one square mile for each family of five and agreed to pay $12 per head and an annuity of $5 per head.
-
September 15, 1874
Acts and Treaties
Treaty 4
Treaty 4 was signed at Fort Qu'Appelle, Saskatchewan, with Cree, Saulteaux (Chippewa) and other First Nations.
-
September 20, 1875
Acts and Treaties
Treaty 5
Treaty 5 was concluded at Lake Winnipeg ceding an area of approximately 100,000 sq. miles inhabited by Chippewa and Swampy Cree (Maskegon) of Manitoba and Ontario.
-
April 12, 1876

Acts and Treaties
Indian Act
The Indian Act is introduced. The Act aims to eradicate First Nations culture in favour of assimilation into Euro-Canadian society. The Act also reinforces that Status Indians must voluntarily give up status and treaty rights to vote federally. Status Indian women are barred from voting in band council elections.
-
August 23, 1876

Acts and Treaties
Treaty 6
Treaty 6 was signed at Carlton and at Fort Pitt with the Plains Cree, Woodland Cree and Assiniboine. It ceded an area of 120,000 sq. miles of the plains of Saskatchewan and Alberta.
-
September 22, 1877

Acts and Treaties
Treaty 7
Treaty 7 was signed at Blackfoot Crossing in southern Alberta by the Siksika, Kainai, Piikani, Tsuut'ina and Stoney. Canadian officials understood that by the treaty First Nations surrendered some 35,000 sq miles of land to the Crown in return for reserves, payments and annuities.
-
January 01, 1885
Acts and Treaties
Electoral Franchise Act
The original draft of the Act gave federal voting rights to some women, but under the final legislation, only men can vote. The Act gives some Reserve First Nations with property qualifications the right to vote, but bars Chinese Canadians.
-
March 03, 1887
Acts and Treaties
Fisheries Retaliation Act
The US passed the Fisheries Retaliation Act, which excluded Canadian vessels from US waters and stopped the importation of Canadian goods.
-
June 21, 1899

Acts and Treaties
Treaty 8
Cree, Beaver, Chipewyan and Slavey First Nations ceded territory south and west of Great Slave Lake in northern Alberta to the federal government in Treaty 8.
-
April 08, 1904
Acts and Treaties
Lansdowne-Cambon Convention
By the Lansdowne-Cambon Convention France surrendered the right of French fishermen to land on certain coasts of Newfoundland to dry fish.
-
July 11, 1906
Acts and Treaties
Lord's Day Act Passed
The Lord's Day Act, officially making Sunday a day of rest in Canada, was passed into law by the Senate. The Act restricted trade, labour and recreation on Sundays.
-
January 11, 1909
Acts and Treaties
Boundary Waters Treaty Signed
The Boundary Waters Treaty was signed by the United States and Canada. Each country pledged that the boundary waters between them would not be polluted to the detriment of the health or property of the other. The treaty also created the International Joint Commission, which controlled water disputes between the signatories and prepared reports on environmental issues relevant to them. The treaty was one of the most significant international agreements of the time, and was a model for environmental dispute resolution.
-
August 29, 1917
Acts and Treaties
Military Service Act
The Military Service Act was passed, making most male British subjects up to 45 years of age liable for active military service (Conscription).
-
September 20, 1917
.png)
Acts and Treaties
Wartime Elections Act and Military Voters Act
Parliament passes the Wartime Elections Act. The right to vote federally now extends to women in the armed forces and female relatives of military men. However, Citizens considered of “enemy alien” birth and some pacifist communities are disenfranchised.
-
June 28, 1919
Acts and Treaties
Treaty of Versailles Signed
The Treaty of Versailles, the peace settlement imposed on Germany after World War I, was signed near the French capital at Versailles. It took effect on January 10.
-
July 01, 1920
Acts and Treaties
Dominion Elections Act
The Dominion Elections Act enfranchised many of those who had been disenfranchised during the First World War, such as those originating from countries with which Canada had been at war. However, the Act stated that anyone who was disenfranchised by provincial legislation because of race would remain disenfranchised from the federal vote. This included persons of Chinese origin in Saskatchewan, and those of Indigenous, Chinese, Japanese, and South Asian origins in British Columbia.
-
March 02, 1923

Acts and Treaties
Halibut Treaty
The "Halibut Treaty" with the US was the first treaty signed independently by Canada, without the participation of an Imperial delegate.
-
February 24, 1925
Acts and Treaties
Lake of the Woods Treaty
Canada signed a boundary treaty with the US, providing for an International Lake of the Woods Control Board.
-
July 20, 1932
Acts and Treaties
Ottawa Agreements
Canada and Commonwealth countries signed 12 bilateral trade agreements in Ottawa providing for mutual tariff concessions and certain other commitments.
-
January 01, 1934
Acts and Treaties
Dominion Franchise Act
Inuit and First Nations persons living on reserves are disqualified from voting in federal elections, except for First Nations veterans who had previously received the vote.
-
April 20, 1941

Acts and Treaties
Hyde Park Declaration
Mackenzie King and F.D. Roosevelt signed the Hyde Park Declaration, uniting the economies of the two countries for war.
-
May 14, 1946
Acts and Treaties
Canadian Citizenship Act Passed
The Canadian Citizenship Act was passed, to take effect 1 January 1947. The Act replaced British subject status with Canadian citizenship.
-
January 01, 1947
Acts and Treaties
Canadian Citizenship Act and repeal of Chinese Immigration Act
Changes to federal legislation allow Chinese and South Asian Canadians to vote. However, it isn’t until 1951 that the final restrictions are lifted in provincial elections Canada-wide.
-
January 01, 1948
Acts and Treaties
Amendments to Dominion Elections Act
Race is no longer grounds for exclusion from voting in federal elections. However, Status Indians still have to give up their Status in order to vote.
-
December 16, 1949
Acts and Treaties
Amendment to BNA Act
The British North America Act was amended by the British Parliament so that the Canadian Parliament would have the power to amend its own constitution.
-
January 17, 1961

Acts and Treaties
Columbia River Treaty
PM John Diefenbaker and President Dwight Eisenhower signed the Columbia River Treaty, dealing with the co-operative development of the Columbia River. It became effective in 1964.
-
September 16, 1964
Acts and Treaties
Columbia River Treaty Effective
The Columbia River Treaty became effective. It was signed in 1961.
-
July 09, 1969
Acts and Treaties
Official Languages Act (1969)
The Official Languages Act was given assent, to come into effect on September 7. It declared English and French the official languages of the federal administration. Federal government services — including all services related to federal elections — must now be available in both French and English. (See Official Languages Act, 1969.)
-
October 23, 1969
Acts and Treaties
Bill 63 (Québec)
Jean Jacques Bertrand's government introduces Bill 63, a controversial language bill that allowed parents the freedom to choose their children's language of instruction.
-
June 26, 1970
Acts and Treaties
Canada Extends Boundary
Canada extended its former three-mile limit to its territorial waters to 12 miles with the passage of the Act to Amend the Territorial Sea and Fishing Zones Act. It was proclaimed August 1, 1970.
-
December 02, 1971
Acts and Treaties
Norway-Canada Agreement
Norway and Canada signed a fishing and sealing agreement. Norway agreed to cease fishing in Canadian territorial waters.
-
April 15, 1972

Acts and Treaties
Water Quality Agreement
Canada and the US signed the Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement.
-
July 31, 1974
Acts and Treaties
Bill 22 Passed
Bill 22 made French the language of civic administration and services, and of the workplace, in Québec.
-
April 17, 1982

Acts and Treaties
Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms
The Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms affirms the right of every Canadian citizen 18 and older to vote and to stand as a candidate.
-
December 15, 1984
Acts and Treaties
Bill 101 Challenged
The Supreme Court of Canada ruled that the compulsory exclusive use of French on public commercial signs, as per Bill 101, was contrary to the right of freedom of speech. The Bourassa government reacted by introducing Bill 178, reinstating the use of French-only signs.
-
July 21, 1988
Acts and Treaties
War Measures Act Revoked
The War Measures Act was revoked and replaced with the Emergencies Act, which prohibits discriminatory emergency orders, permits Parliament to override the emergency orders of the government, requires an inquiry into the actions of the government after any emergency and provides for compensation to the victims of government actions.
-
June 28, 1991
Acts and Treaties
BC Treaty Commission Created
Federal, provincial and First Nations representatives agreed to create a treaty commission to co-ordinate treaty negotiations in BC, marking a fundamental change in the provincial government's policy toward First Nations.
-
October 04, 1993
Acts and Treaties
BC Freedom of Information and Protection of Privacy Act
The BC Freedom of Information and Protection of Privacy Act, hailed as one of the strongest in the world, was proclaimed.
-
March 11, 1999
Acts and Treaties
Death of Camille Laurin
Camille Laurin, psychiatrist, politician and president of the executive committee of the Parti Québécois, died at Montreal. Author of the white paper declaring French as the only official language of government, education and business in Québec, Laurin was known as the father of Bill 101.
-
June 30, 1999

Acts and Treaties
Treaty to Share Pacific Salmon
Canada and the US signed a treaty governing the conservation and sharing of Pacific salmon, which migrate between waters of the two nations.
-
September 13, 2018

Acts and Treaties
Agreement Reached in Williams Treaties Dispute
In 1992, the seven Williams Treaties First Nations filed a lawsuit against the federal government asking for financial compensation for land surrenders and loss of rights dictated by the Williams Treaties. Ten years later, a trial began in which Canada and Ontario acknowledged limited off-reserve treaty harvesting rights, but litigation was dropped in favour of out-of-court negotiations. These began in March 2017. A negotiated settlement approved on 13 September 2018 gave financial compensation to the First Nations involved. It recognized their harvesting rights and allowed each First Nation to add up to 4,452 hectares to their reserves by purchase from willing sellers.



