Article
Remembering the walrus hunt
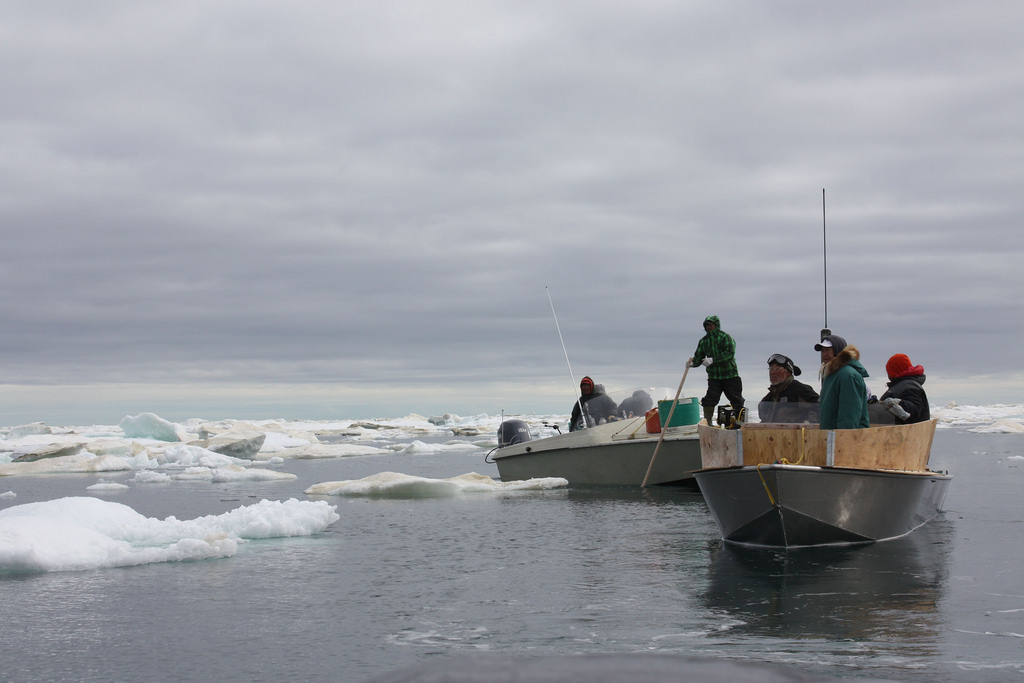
The Aivilingmiut of Nunavut are walrus hunters. Like many regional groups of Inuit, they’re named after the animal that once kept them alive.

Enter your search term
Signing up enhances your TCE experience with the ability to save items to your personal reading list, and access the interactive map.
Create AccountArticle
The Aivilingmiut of Nunavut are walrus hunters. Like many regional groups of Inuit, they’re named after the animal that once kept them alive.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/b0be7080-64dd-42a1-b455-dcf920df8bfa.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/b0be7080-64dd-42a1-b455-dcf920df8bfa.jpg

Article
Revolutionary industrial unionism, or syndicalism, a broad international movement dedicated to organizing all workers into single, unified labour organizations designed to overthrow the capitalist system by means of industrial actions, including the general strike.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Editorial
The following article is an editorial written by The Canadian Encyclopedia staff. Editorials are not usually updated. In late October of 1929, terror seized the stock exchanges of North America. Capitalism’s speculative party, with its galloping share prices and its celebrity millionaires, came to an abrupt stop. The Great Crash, it was called, and it was followed by the Great Depression.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/cc8df85f-c925-4f6f-91e1-7403bcb85345.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/cc8df85f-c925-4f6f-91e1-7403bcb85345.jpg

Article
Wood was the staple of Canadian trade for much of the 19th century. Fueled by European demand, the timber trade brought investment and immigration to eastern Canada, fostered economic development, and transformed the regional environment far more radically than the earlier exploitation of fish and fur (see Fisheries; Fur Industry). It encouraged exploration, the building of towns and villages, and the opening of roads. While a great resource for Canada, timber also contributed at times to economic instability. Over the course of the industry’s history, weather conditions, commercial uncertainties and imperfect market intelligence produced wide fluctuations in the demand for—and the price of—wood.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/timbertradehistory/lumbercamp.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/timbertradehistory/lumbercamp.jpg

Article
The trading post can be viewed as a large household whose size and social organization reflected the cultural heritage of its members and the post's role in the fur trade.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/a4d6e476-5e53-4126-9ee6-313b64235660.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/a4d6e476-5e53-4126-9ee6-313b64235660.jpg
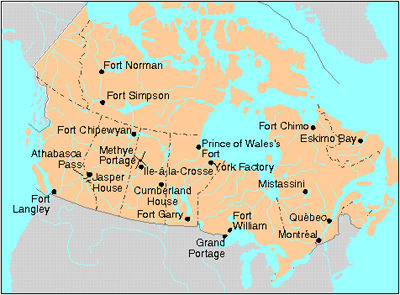
Article
The triangular trade was a trade route connecting France, New France and the West Indies. It was established by France’s comptroller general of finance, Jean-Baptiste Colbert, and applied in Canada in 1667 by Jean Talon, the intendant of New France. The triangular trade enabled New France to diversify its economy and establish its position on the international trade networks.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/0525a218-565d-4cb9-9eb4-045638ce2140.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/0525a218-565d-4cb9-9eb4-045638ce2140.jpg

Editorial
The following article is an editorial written by The Canadian Encyclopedia staff. Editorials are not usually updated.At some point in the 1650s, two adventurers from New France embarked on a journey that eventually revolutionized the fur trade and changed the course of Canadian history.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
In the 18th century, British and American ships cruised the Atlantic seaboard. In the 19th century, Canadians entered the field, establishing a whaling station in Newfoundland, and taking whales as part of a deep-sea fishery operation from Gaspé.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
Women are considered labour force participants only if they work outside the home. In the past women have been expected to be in the labour force only until they marry; this reflects the historical, idealized notion of a society in which the man is the breadwinner and the woman the homemaker.
"https://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/57bf0875-fdbe-4d5c-8309-1ab4037ceaeb.jpg" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://d3d0lqu00lnqvz.cloudfront.net/media/media/57bf0875-fdbe-4d5c-8309-1ab4037ceaeb.jpg

Article
Women's Labour Leagues emerged in Canada prior to WWI. Modelled on the British Labour Leagues, auxiliaries to the Independent Labour Party, their purpose was to defend the struggles of women workers and support the labour movement.
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9

Article
Workers Unity League the Workers Unity League (WUL) is a national trade union federation that was formed in 1929 on the initiative of the Communist Party Of Canada in line with the decision of the Communist International (Comintern) in 1928 that communists break with their previous policy of working inside existing labour parties and labour unions to push for more militant stances. The new policy stressed the need for revolutionary organizations independent of the existing...
"https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9" // resources/views/front/categories/view.blade.phphttps://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/images/tce_placeholder.jpg?v=e9dca980c9bdb3aa11e832e7ea94f5d9
