Article
Patriation Reference
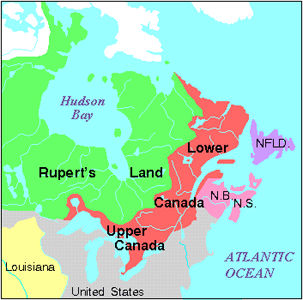
The Patriation Reference, formally known as Re: Resolution to Amend the Constitution, was a reference case of the Supreme Court of Canada. On 28 September 1981, the court decided that it was legal for the federal government to patriate and amend Canada’s Constitution without the consent of the provincial governments. But it also found that to do so in areas that affect provincial powers would be a breach of constitutional convention. The court’s decision concluded that such conventions are of great significance. In the words of the court, “Constitutional convention plus constitutional law equal the total constitution of the country.”